Whether you are using it on Windows, Linux or Mac OS, Google Chrome is free, easily available and comes along a number of development tools for software developers. It is not just a web browser but also a complete package for both your desktop and phones. It’s simple yet fascinating interface is fast, secure and includes Google’s smart built-in extensions and themes to make your working experience a whole lot better.
Google Chrome 73 Stable Version
With the recent release of its 73 stable version, Google Chrome’s new update is now thoroughly tested and enhanced with a variety of features. After storming the internet world on March 12, 2019, Google’s new browser has attracted a lot of media attention.
What’s new in the new Google Chrome?
Google standout features have always been on point. So is the case with its new browser. With a built-in dark mode, media key support and tab grouping, Google Chrome 73 is set to beat all its previous versions.
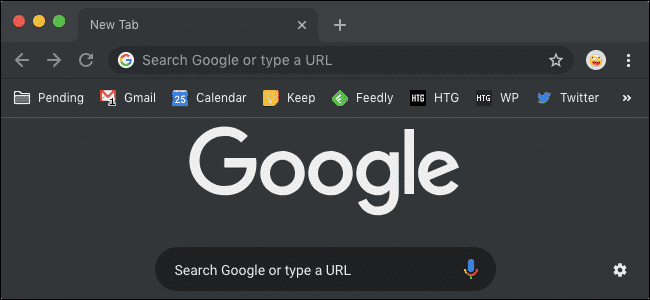
A glimpse of how the dark mode looks like. Although, it looks more like Google’s incognito mode, but still will be much better than the boring white mode.
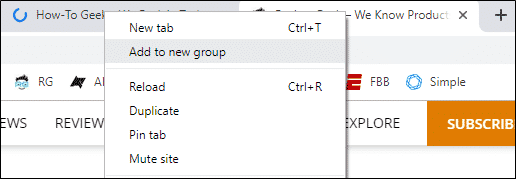
Another interesting feature called Tab Grouping will let you arrange your tabs in the form of the group so you could stay organized while working. It is a great feature for those who open 20+ tabs at the same time! Let’s see how this turns out in practice.
How to Update your Chrome Browser?
The new version will be available for mobile operating systems such as Apple and Android, and Desktop OS including Windows 10 and above, Ubuntu 18.04 LTS and 16.04 LTS and Linux Mint 19/18.
To update Google Chrome on any of your Ubuntu versions from the above, follow the steps below:
Option 1: Update Using Google Repository
Step 1: Add Google Chrome Repository
For users relying on the Ubuntu Terminal for most of their work can follow the simple commands to update to the latest Google Chrome Version using Google repositories from their official sources. For this, you will first need to create a file named “google-chrome.list” in the directory with the path link “/etc./apt/sources.list.d”.
To do that, type the following command in the terminal:
Now download the repository into your system:
Next, add the repository to the file you have created. You can add it according to your system architecture.
For 64-Bit Systems:
Type the following command in the terminal:
http://dl.google.com/linux/chrome/deb/ stable main" >>
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/google.list'
For 32-Bit Systems:
Type the following command in the terminal:
http://dl.google.com/linux/chrome/deb/ stable main" >>
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/google.list'
Step 2: Update Google Chrome on Ubuntu 18.04 Versions
Once you have added the Google Chrome repository into your system, use the commands below to update it to the latest stable version. If you have Chrome already downloaded in your system, the execution will update it to the newer version else it will install Google Chrome 73 if you don’t have the browser in the first place.
Type the following commands in the terminal:
Note:
For users who don’t want to get started with the stable version straight away can update their Google Chrome browser to beta or unstable versions too. To do that, type in the following commands:
Beta Version
Unstable Version
Step 3: Launch the Updated Google Chrome Browser
After successfully executing the commands in the first two steps above, you will now have the updated version installed on your system. You can either search for Google Chrome through Ubuntu’s graphical user interface or launch it through the Terminal. Follow the commands below:
google-chrome-stable &
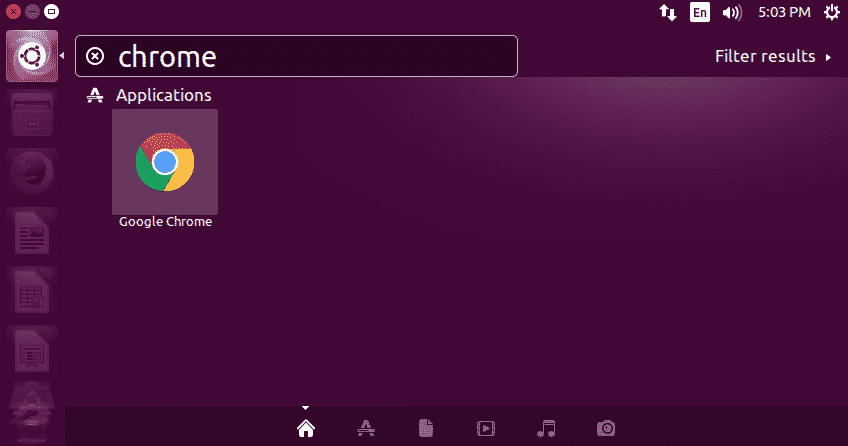
You will find the Chrome icon when searching through the Graphical User interface like this:
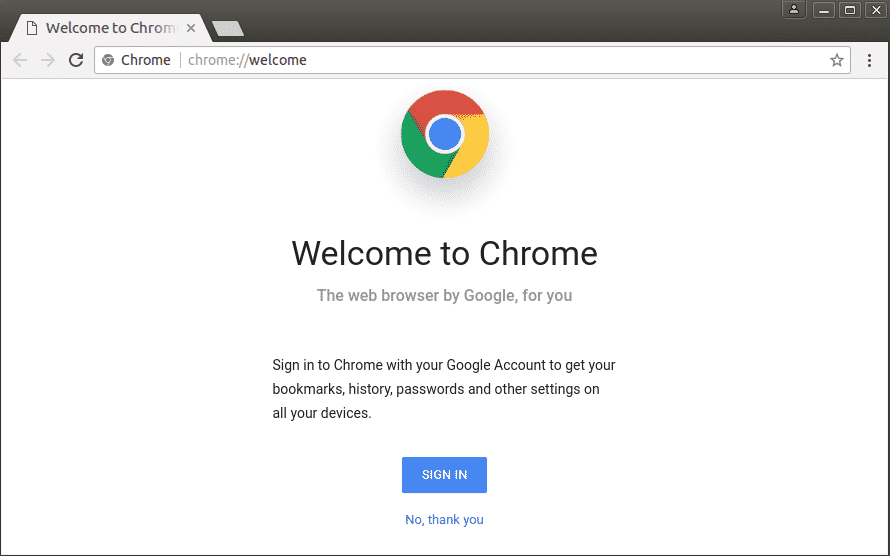
Google Chrome 73 stable version after launching will appear like this:
OPTION 2: Manually Install through Debian Package
Users who are familiar with the Ubuntu environment would find the first process comparatively easier and understanding. Meanwhile, others who are new to the command-driven interface would find difficulties in understanding commands and executing them.
A simple and user-friendly approach to update Google Chrome is by downloading the .deb package from the website and then installing it through dpkg package manager.
To start off, download the package from Google Chrome’s official website (https://www.google.com/chrome/).
Then, install it using the following commands:
sudo dpkg -i google-chrome*.deb
sudo apt-get install -f
Make sure you follow each step carefully and type each command correctly with the designated spaces in between.
After successfully installing the package, run the new Google Chrome browser via terminal using the command below:
Note: if you are working on multiple apps simultaneously and want to run Chrome in the background, then use this command:
The process above will automatically add a PPA (Personal Package Archive) to your system, which will let Google Chrome receive latest updates and notify you in the future.
Lastly, if you want to remove Google Chrome Browser from your system, you can easily do it through the terminal. For that, type in the following command: