It is often necessary to perform calculations depending on user inputs when creating a Bash script. Throughout this guide, before carrying out a basic operation with a shell script, first, let’s take a glance at interpreting and verifying user inputs. We will be using the integrated Bash read command to interpret the Bash user input. The read command takes some value as input via the user and allocates it to the variable. It read out only a solitary line through the Bash command terminal. In this guide, you would learn how to interpret the user input from the terminal and the script.
To implement the read command, here is the syntax:
Example 01:
Let’s take a simple example of reading input from the user in bash when prompt. Open a terminal and create a new file “input.sh”.
Open the file and add a little code to it as below. Firstly, the echo statement is asking the user to add input value. The read statement is used to input user value, which will be saved to the variable “NAME”. The last echo statement is used to print the answer with inputted value as “$NAME” variable.
Execute the file using the bash command. Firstly it will prompt for the name. When the user inputs the value “Aqsa”, it will print the message with the value within it.
Example 02:
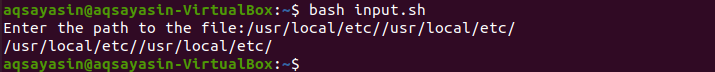
Open the old file and write the below code into it. We may be using the integrated read command; to a user with a query, using that -p option. You have to summon up to use the “readline” keyword -e to let line editing with arrow keys. After that, use the variable to print the path of a file entered by a user at the command shell.
Let’s check the output of this code using the bash command in the terminal. You will see it will ask for the file path to be entered in the shell. When you enter the required value and press Enter, it will print it out.
If you want to suggest an answer, you have to use the keyword “–i” after the string with the path in inverted commas.
Let’s check the output for updated code using the bash command. You will perceive that it will suggest you a file path as below.
Example 03:
Let’s have another example of prompting for input in a shell. Write down the below code in the file “input.sh”. We have two read commands to add login credentials by a user on the shell. The keyword “-sp” is used to hide the credential “Password” while entering the shell.
On execution, you can see that the user has entered its credentials while the password is hidden while entering. In the end, it has displayed the message to pay thanks to the user.
Example 04:
We have another example to read multiple car names as values from the user’s bash shell. For this purpose, we required three variables as “car1”, “car2”, and “car3”. We have an echo comment that is asking for the names of cars. Read command is used to read inputted values (names of cars) by a user in a shell. The next three echo statements will print the messages with the names of the car consecutively.
Using the bash command, execute the file. It will ask for the names of cars you like. When the user entered the names of cars consecutively, it will save them into variables of a read command and print them out by using the next three echo statements one by one.
Example 05:
In the above example, we have seen how to prompt user input while saving the input into three variables. In this example, we will learn about how to read user inputted values in one variable as array members using the keyword “-a”. So, open the same file and write the below code in it. The echo statement will ask you to enter the input required. The read statement has the keyword “-a” to take multiple values from the user and save them to the one variable array “NAMES”. At the last echo statement, all the inputted values are printed as array members within the string text.
While running the file “input.sh”, the user has been prompted to enter the values. When the user enters the values, these values have been saved into the array variable “NAMES”. After saving these values, the echo statement will be executed and print out the inputted names as array values within itself as shown.
Example 06:
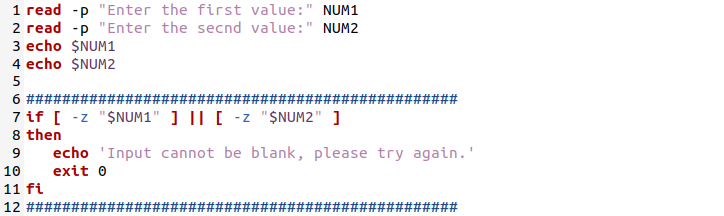
Let’s take the same file with little change in the script. We have written two read commands to take value from a user as input in a shell and saved them in two variables, “NUM1” and “NUM2”. After that, both the variables have been printed out.
In the command terminal, write the Chmod command to assign execution privileges to this file.
When you execute this file using bash, you will see it will prompt you to add numbers consecutively. When you enter the required values, it will print out both numbers separately.
If you want to validate that any field or variable is left blank by the user, you can update the previous code as below. The keyword “-z” is used to check both variables, if they have any blank spaces in them.
While the execution, the user has added space as a number. The user got a message to try again because the variable entered by the user got spaces.
Let’s try the same code with some conditions over the numbers inputted by the user. If the user input’s any character other than those mentioned in the below code, it will pass a message.
While trying this code, a user has added one special character, which generates a prompt message.
Conclusion
In this guide, you have successfully learned how to prompt user input in the shell and interpret the user input using some very simple examples.