This is where the concepts of Modularity and Code Reusability come into play. Modularity, or modular programming, is a highly recommended programming approach that breaks code into chunks to enhance readability, which also results in Code Reusability. Code Reusability refers to the ability to reuse a certain piece of code repeatedly, thus avoiding the task of rewriting the code every time it is used.
Modularity and Code Reusability are why functions are so extensively used in all programming languages, regardless of whether they are high-level or low-level. However, it can be quite tricky to create functions that work with the correct arguments or that accept certain arguments. This article uses several examples to show you how to create Bash functions with arguments in Linux Mint 20.
Examples of Creating Bash Functions with Arguments in Linux Mint 20
Functions with arguments in Bash can be created very conveniently. The following examples demonstrate how to create various Bash functions with arguments.
Example 1: Passing a String Argument to a Function
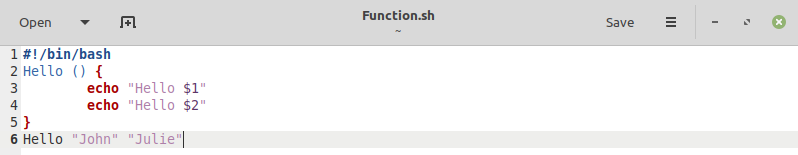
In this example, we will write a Bash script that will define a function to take a string as an argument. This can be done by copying the script shown in the image below in a Bash file. You can name your Bash filename according to your preferences:
In this Bash script, we created a function named “Hello.” Inside the body of the function, we will print a message, followed by “$1,” which represents the value of the string argument that will be passed to this function. Then, outside the body of this function, we called this function with its name while specifying the string argument to be passed to the function inside of double-quotes.
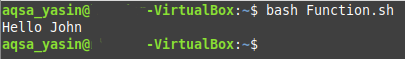
After creating this Bash script, we will execute the script with the following command:
The output of this script is shown in the image below:
Example 2: Passing More than One String Argument to a Function
In the next example, we will write a Bash script that will define a function to take two string arguments. This can be done by copying the script shown in the image below in a Bash file:
The script used in this example is roughly the same as the one that we wrote in our first example. The only variation is that, in this script, we used two placeholders (i.e., “$1” and “$2”) for our arguments, since we are passing two string arguments to this function. Then, in the same manner, we called this function with its name, followed by two string arguments enclosed in double-quotes.
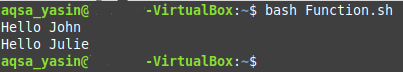
After executing this modified script, you will obtain the following result:
Example 3: Passing Integer Arguments to a Function for Addition
To add two integers in Bash, we will write a Bash script that will define a function to take two integer arguments. This can be done by copying the script shown in the image below in a Bash file:
In this Bash script, we defined a function named “Sum.” Inside the body of this function, we created an expression to add the values of the integer arguments “$1” and “$2” and store the result of the sum in the variable “add.”
We will display the result of this calculation using the “echo” command. Outside the body of this function, we called it with its name, followed by the two integer parameters, “22” and “27.”
When we execute this Bash script, we will obtain a message in our terminal, followed by the result of our addition, which will be “49.” The output of this script is shown in the following image:
Example 4: Passing Integer Arguments to a Function for Multiplication
To multiply two integers in Bash, we will write a Bash script that will define a function to take two integer arguments. This can be done by copying the script shown in the image below in a Bash file:
In this Bash script, we defined a function named “Product.” Inside the body of this function, we created an expression to multiply the values of the integer arguments “$1” and “$2” and store the product in the variable “mul.”
Then, we will display the result of this calculation with the “echo” command. Outside the body of this function, we called it with its name, followed by two integer parameters “2” and “3.”
When we execute this Bash script, we will obtain a message in our terminal, followed by the result of our multiplication, which will be “6.” This output is shown in the following image:
Conclusion
This tutorial showed you four different examples of creating Bash functions with arguments. These examples were based on the functions that display messages, as well as those that perform some basic calculations. With these examples, you should now have a basic idea of passing arguments to functions in Bash in Linux Mint 20. However, the complexity of these functions can vary according to the requirements of your program.