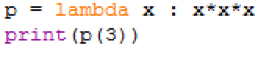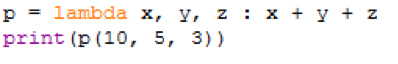In this article, we will try to learn about Python Lambda.
Definition
Lambda is a function defined without a name. This can take multiple arguments, but only one expression is allowed that is evaluated and returned. Where function objects are required, we can use the lambda function.
Syntax:
lambda arguments: expression
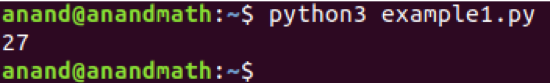
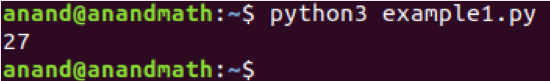
Example 1: The function below is used to calculate the cube of a number.
return a*a*a
print(cube(3))
The above function can be written using lambda, as shown below:
print(p(3))
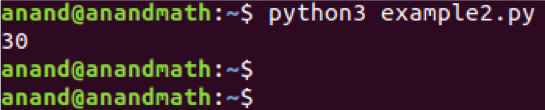
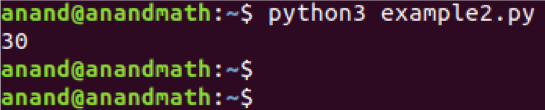
Example 2: The function below is used to calculate the sum of two numbers.
return x + y
print(sum_2(10,20))
The above function can be written using lambda, as shown below:
print(p(10,20))
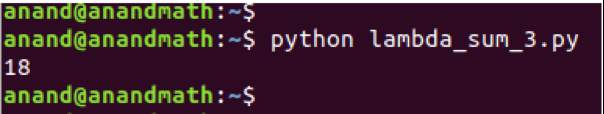
Example 3: The example below for lambda takes multiple arguments.
print(p(10, 5, 3))
Example 4: This function multiplies the number by 2 and can be written using Lambda function as below:
return lambda x : x * n
multiply_by_2 = func(2)
print(multiply_by_2(11))
print(multiply_by_2(15))
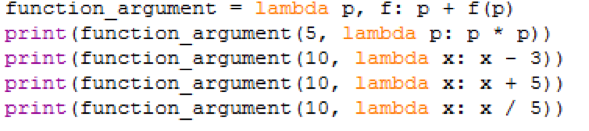
Example 5: The function takes function as an argument and returns the result.
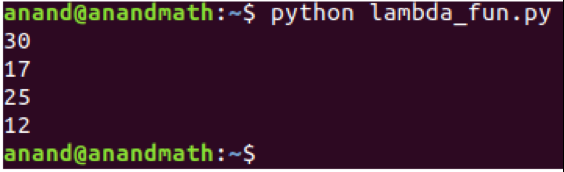
print(function_argument(5, lambda p: p * p))
print(function_argument(10, lambda x: x - 3))
print(function_argument(10, lambda x: x + 5))
print(function_argument(10, lambda x: x / 5))
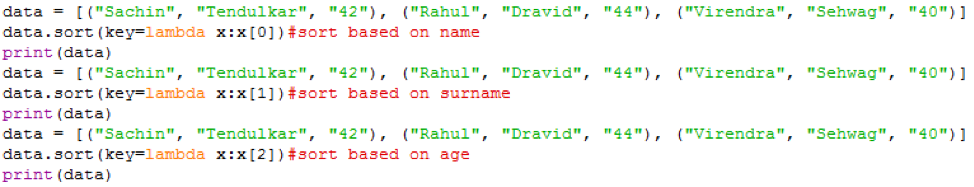
Example 6: In the example below, lambda is used to sort the values.
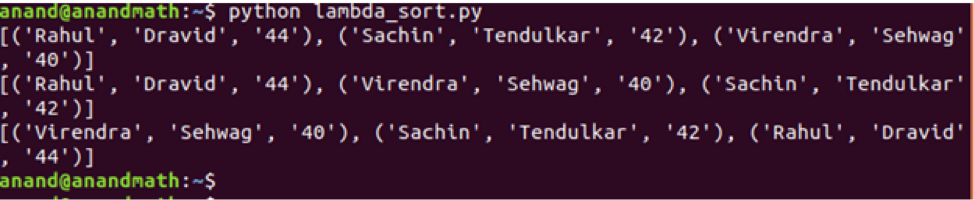
data = [("Sachin", "Tendulkar", "42"), ("Rahul", "Dravid", "44"), ("Virendra", "Sehwag", "40")]
data.sort(key=lambda x:x[0])#sort based on name
print(data)
data = [("Sachin", "Tendulkar", "42"), ("Rahul", "Dravid", "44"), ("Virendra", "Sehwag", "40")]
data.sort(key=lambda x:x[1])#sort based on surname
print(data)
data = [("Sachin", "Tendulkar", "42"), ("Rahul", "Dravid", "44"), ("Virendra", "Sehwag", "40")]
data.sort(key=lambda x:x[2])#sort based on age
print(data)
Now, go into python3 interpreter.
The lambda function is used in many inbuilt methods. The following are some examples:
1. Map
This function maps each element in sequence using the lambda function.
Syntax:
map(function, seq)
Ex:
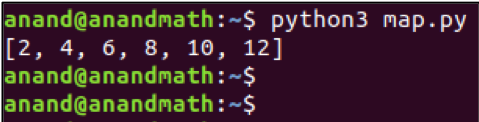
nums = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
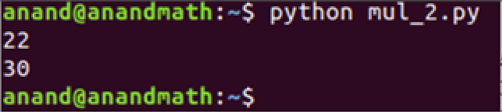
Here, we will multiply each element in the list by 2.
mul_2 = map(lambda x: x*2, nums)
print(list(mul_2)) # It returns map object and typecasting it as list.
In the above function, each element of thelist is passed to the lambda function and the lambda function will multiply it by 2.
mul_2 = map(lambda x: x*2, nums)
print(list(mul_2))
2. Filter
This function filter out all the elements of a list for which the lambda function returns True.
Syntax:
filter(function, seq)
Ex:
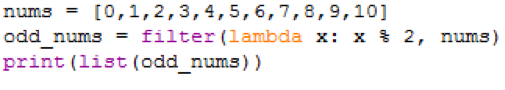
nums = [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
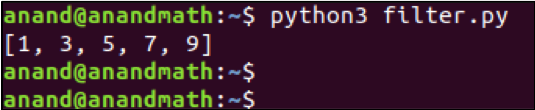
odd_nums = filter(lambda x: x % 2, nums)
print(list(odd_nums)) # It returns map object, and typecasting it as list.
odd_nums = filter(lambda x: x % 2, nums)
print(list(odd_nums))
3. Reduce
This function returns a single value by applying function func() to the seq.
Syntax:
reduce(func, seq)
Ex:
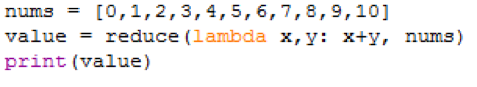
nums = [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
value = reduce(lambda x,y: x+y, nums)
print(value)
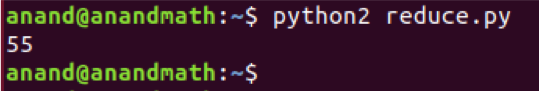
In the above list, it will take the first 2 elements and perform addition. The result of an addition will be added to the third element and so on. Finally, it will return a single value.
Note: This method is not available in the python3+ version.
value = reduce(lambda x,y: x+y, nums)
print(value)
Conclusion
From this article, we have learned many aspects of the lambda function. Depending on what the program needs, we can use it and make better python coding. This is most commonly used to pass arguments to another function (for example, we have seen above functions map, filter, and reduce).