Definition
In Python, a file is a location on disk used to store information, which some names are associated with it. It is used to store data permanently in a non-volatile (non-volatile means retains data even if power loss) memory (Ex: hard disk).
Syntax
file_pointer = open(filelocation, modes, encoding= encoding_type)
encoding is an optional parameter
Files can be opened in any of the following modes:
- r –> read mode
- w –> write mode
- a –> append mode
- + -> append this to the above modes to open the file for reading and write modes Ex: r+
To open a file in binary mode append “b“ to the above modes.
Ex: To open the file a binary file in readmode use “rb“.
How to enter into python interpreter?
Open Linux terminal and type “python” and hit enter so we will see python interpreter. For python3+ version type “python3”, we are going to see the following info on the terminal. If we want to check the Python version, type “python -v”.
In Python a file, this operation is performed in the following order:
- Open a file
- Read or write or append: When we specify write mode, the file will be opened in write mode if it exists, otherwise, it is going to create the file. This is applicable for append mode also. In read mode, if file exists, it opens in the read mode, otherwise, throws FileNotFoundError exception.
- Close the file
Open a file
Inbuilt method open() used.
Ex:
f = open("textfile.txt",'w') # write in text mode
f = open("abc.bmp",'r+b') # read and write in binary mode
Closing a file
Inbuilt method close() used.
Ex:
# perform some file operations
fp.close()
Safer way to open and close files using exception handling:
fp = open("textfile.txt",'r',encoding = 'utf-8')
# perform some file operations
finally:
fp.close()
Using this method, we are making sure that the file is closed always.
File operations using with
The best way to perform file operation and most commonly used method with statement. Using this ensures that the file is closed when the block inside with is exited.
Ex:
#perform some file operations
#statements outside the with block
When we exit with block, the file will be closed automatically.
Write to File
To write into a file, we need to open it in write ‘w’ or append ‘a’.
To write to a file, python has the following inbuilt methods:
write(): This method writes the string to a file.
Ex:
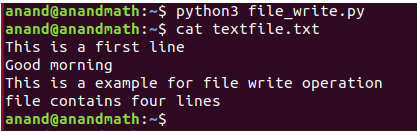
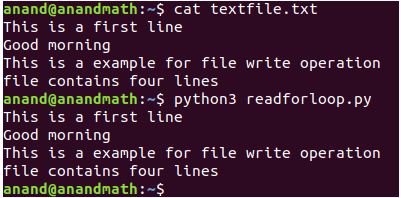
f.write("This is a first line\n")
f.write("Good morning\n")
f.write("This is a example for file write operation\n")
f.write("file contains four lines")
If we open the textfile.txt file, we see the above lines are written successfully.
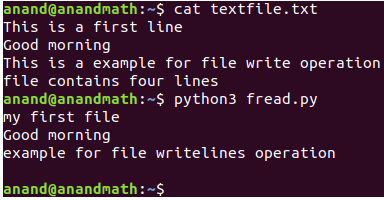
writelines() : This method writes the list of strings to a file.
Ex:
"This is a example for file write operation\n",
"file contains four lines"]
with open("textfile.txt",'w',encoding = 'utf-8') as f:
f.writelines(file_content)
Reading from file
To read a file in Python, we must open the file in reading mode ‘r’.
To read from a file, python has the following inbuilt methods:
read():
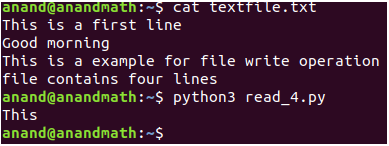
read(4): This method reads the first 4 characters from the file.
Ex:
print(fp.read(4))#It will read first 4 characters
fp.close()
read() : This method reads till end of file.
Ex:
print(fp.read())#It will read till EOF
fp.close()
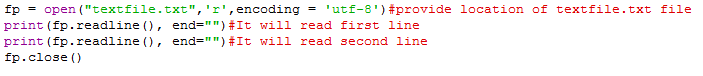
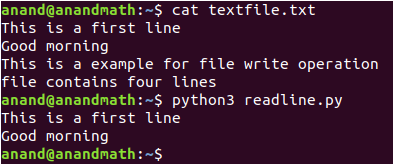
readline(): This method reads one line at a time.
Ex:
print(fp.readline(), end="")#It will read first line
print(fp.readline(), end="")#It will read second line
fp.close()
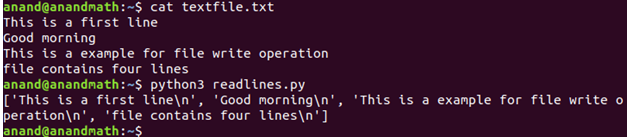
readlines(): This method read all lines in the file and returns a list.
Ex:
print(fp.readlines())# read all ines in the file
fp.close()
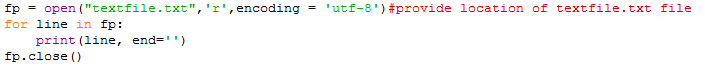
for loop: This is the most commonly used way of reading a file. We can read a file line by line using a forloop. This is an efficient and fast way of reading a file.
Ex:
for line in fp:
print(line, end='')
fp.close()
Traverse in a file
The following methods are used to traverse in a file.
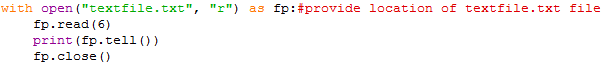
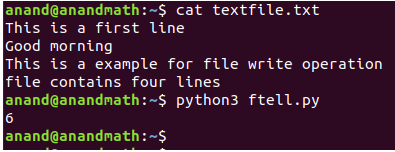
tell(): This method is used to get the current file position in a file.
Ex:
fp.read(6)
print(fp.tell())
fp.close()
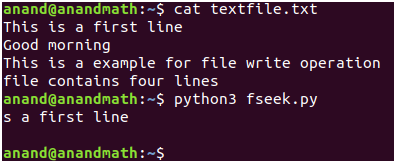
seek(): This method used to bring/place file cursor to a given position in a file.
Ex:
fp.seek(7)
print(fp.readline())
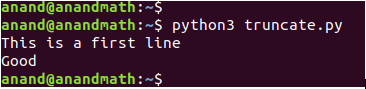
truncate(): This method is used to modify/resize the file to a specified size in a file.
Ex:
with open("textfile.txt",'w',encoding = 'utf-8') as f:
f.write("This is a first line\n")
f.write("Good morning\n")
f.write("This is a example for file write operation\n")
f.write("file contains four lines")
#Apply truncate method
fp = open("textfile.txt", "a")#provide location of textfile.txt file
fp.truncate(25)
fp.close()
#reading the file after the truncate
fp = open("textfile.txt", "r")
print(fp.read())
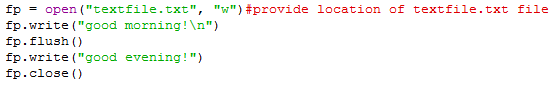
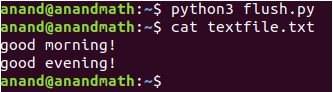
flush() : This method flush/clear a buffer.
Ex:
fp.write("good morning!\n")
fp.flush()
fp.write("good evening!")
fp.close()
Conclusion
In Python, a file is a location on a disk that is used to store information. File handling in Python is simple and easy. Also, in Python, different modules are available for handling different typess of files.
Ex:
| File type | Python module |
|---|---|
| csv | csv |
| xml | xml |
| excel | xlrd |